Low Carb Diet – An Ultimate Guide For Beginners!

Carbohydrates are typically restricted to a low-carb diet, such as those found in sweet foods, pasta, and bread. You cut back on carbohydrates and up your intake of protein and vegetables. Weight loss and improved health markers have both been linked to low-carbohydrate diets.
These diets have been widely followed for decades, and many medical professionals have advocated for them. Furthermore, you won’t have to worry about calorie counting or buying any unique ingredients. Eating a diet composed solely of whole foods is all that is required.
Can You Lose Weight Eating Low Carbs?
Unfortunately, many people now fear gaining weight because of their diets because of the stigma attached to dietary fat. We’ve grown extremely cautious about our fat consumption, often opting for “low fat” options or keeping careful tabs on the number of grams of fat in our daily diets and considering that both the American Heart Association and the United States government advocate for low-fat diets, this makes perfect sense.
Health can be maintained without a low-fat diet. A low-carbohydrate diet is another good choice for losing weight and improving your health. Low-carb diets like the Atkins and South Beach plans, and keto and ketogenic variations are nothing new. While low-carb diets may be popular, they are no longer a fleeting fad.
Recent studies have indicated that a diet low in carbohydrates can positively affect health, but low-fat diets may not be the best option for everyone. When it comes to diet and way of life, there is no universal solution.
For this reason, it is crucial to learn as much as possible about your choices. In the next section, find out how the low-carb diet can help you achieve your goals. Whether you’ve already decided to try a low-carb diet or are simply curious about how it works, this primer is a beautiful place to begin!
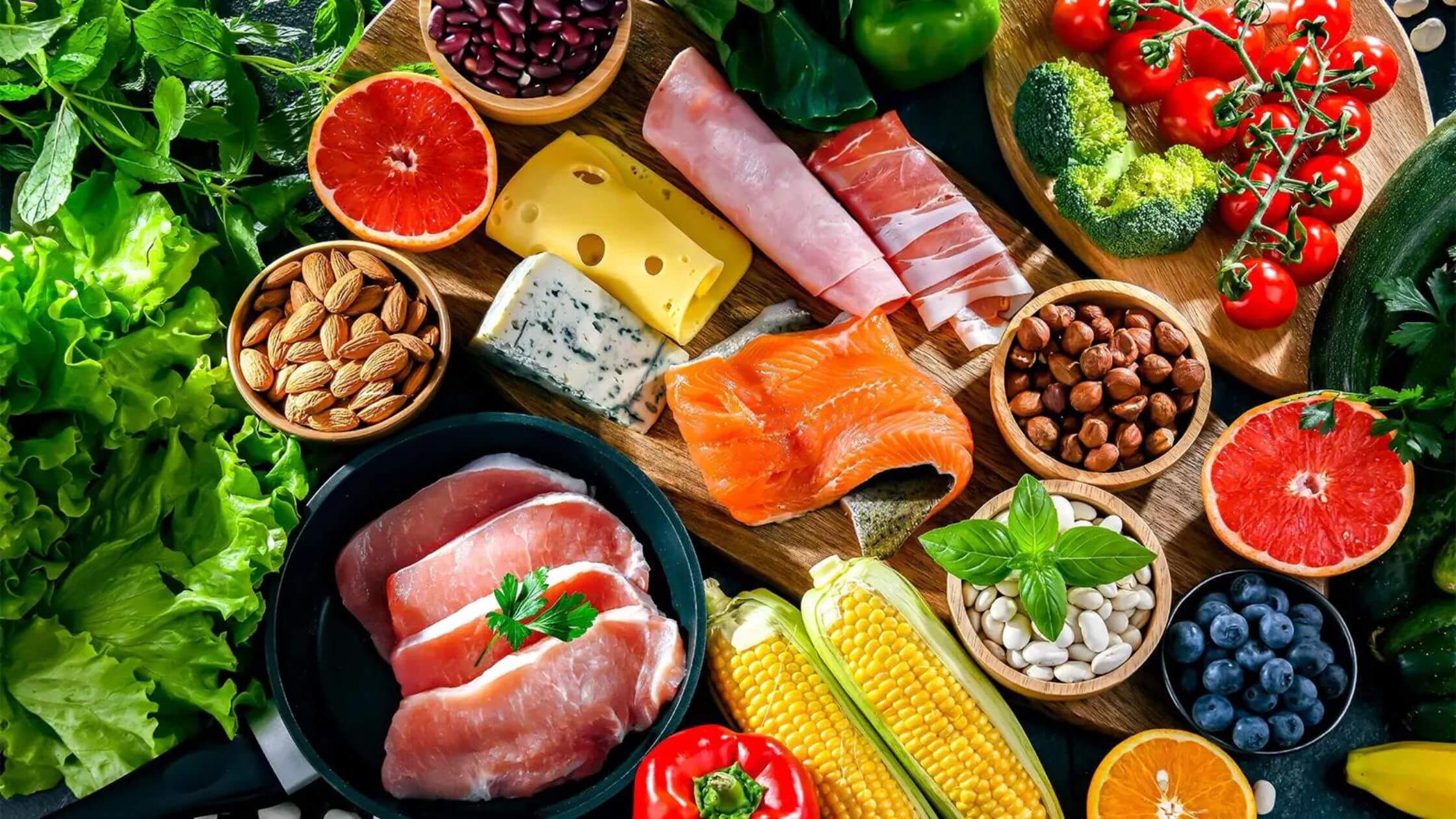

What is a Low-carb Diet?
You can think of a low-carb diet as one in which the proportion of protein and fat you consume increases while the carbohydrate content decreases. ketosis doesn’t happen with every low-carb diet. We’ve been told that fat is bad for us for a long time.
However, “diet” foods that are low in fat are often high in sugar and may be found on nearly every shop shelf. In retrospect, it’s clear that this was a huge blunder, given it co-occurred as the obesity epidemic started.
The widespread availability of low-fat alternatives does not show causation, but it is evident that the low-fat message did not stop the rise in obesity; thus, we feel it has contributed.
A low-carb diet focuses on eating plenty of fresh, low-carb veggies and healthy fats. This eating plan is neither a “meat and cheese” nor a “no carb” approach.
Despite its reputation as a “low carb” diet, the South Beach Diet has significantly more carbohydrates than the standard low-carb diet. Many devotees of the popular but controversial Trim Healthy Mama (THM) diet claim that it is not a low-carb diet but rather a hybrid of several different eating plans.

Each diet has its name and set of tenets, but they all focus on cutting back on carbohydrates and favoring high-quality, whole foods. A low-carbohydrate diet has been shown to aid in weight loss, maintenance, and the prevention of Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes. In order to use fat instead of glycogen (the body’s primary fuel source), a low-carb diet requires you to deplete your glycogen levels.
Lipolysis refers to using fat as fuel, and ketone bodies are the byproducts. For those with healthy metabolisms, this occurs naturally during nighttime fasting (sleep).
Epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, and even cancer have all been treated with ketogenic diets in recent years. Dietary ketones produced by the lipolysis of fat provide a reliable and sustained energy source for people on a ketogenic diet.
There is a common misunderstanding that dietary ketones are the same as the deadly metabolic condition of diabetic ketoacidosis, primarily affecting people with Type 1 Diabetes. (Diabetic ketoacidosis develops When insulin synthesis falls short, and glucose levels in the blood remain elevated, forcing the body to metabolize fat and muscle.
The accumulation of ketones in the blood leads to an acidic blood PH. The current research suggests that we no longer need to fear naturally occurring fats. If you follow a low-carbohydrate diet, on the other hand, you won’t have to worry about your fat intake.
You can consume as much natural fat as you like if you restrict your intake of sugar and carbs and prioritize eating enough protein or even a lot of protein. It may be easier to burn fat stores if you eliminate sugar and carbs, as this helps to regulate blood sugar and reduce insulin levels.
A higher protein intake and the presence of ketones (if eating very low carb) may make you feel fuller, resulting in naturally decreased food intake and boosting weight loss.
Types of Low-carb Diets
1. The Paleo Diet
- Foods on a Paleo diet are meant to resemble those that would have been eaten during the Paleolithic period (about 2.55 million to 10,000 years ago).
- The majority of a primitive person’s diet would have consisted of wild game, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.

This drug may help health:
- A lower carbohydrate and sugar intake in the diet leads to weight loss.
- Insulin sensitivity has improved.
- Benefits of heart health include:
- You’ll have more energy that lasts longer.
- Reduced swelling
Meals like the Thai Turkey Lettuce Cups and the Green Goddess Steak Salad with Roasted Carrots are fantastic options for those following the Paleo diet and are available.
2. The Vegetarian Diet
Vegetarianism is a lifestyle choice in which meat, fish, and fowl are not included in one’s daily diet. As a replacement, you’ll eat more plant-based foods, including grains, veggies, and fruits. Many people adopt this diet for moral or ethical grounds, including concerns about animal rights and environmental impact.

Among the possible advantages are the following:
- Because you’ll consume fewer calories overall, you can lose weight and keep it off.
- There will be less risk of cardiovascular disease because saturated fat and cholesterol will be reduced in your diet.
- Controlling hypertension with a plant-based diet has been shown to help reduce blood pressure.
- It enhanced insulin sensitivity.
- Decreased likelihood of developing metabolic syndrome.
Foods that adhere to the Vegetarian diet, such as these Vegetarian Burrito Bowls and this Vegetarian Potato Soup, are plentiful and delicious.
3. The Vegan Diet
- Veganism is a lifestyle in which no forms of animal exploitation are tolerated.
- Vegans abstain from animal-based food, including meat, fish, poultry, eggs, honey, gelatin, and dairy.

Possible advantages include:
- Loss of body fat as a result of the high-fiber and low-saturated-fat nature of the regular diet.
- There is a greater emphasis on foods like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, beans, peas, nuts, and seeds, which leads to higher consumption of certain essential nutrients.
- Reduce glucose levels in the blood.
- Reduced danger of cardiovascular illness.
- Vegans looking for meal plans and grocery shopping services need to go no further than Farm Fresh to You.
4. Ketogenic
A ketogenic diet (or Keto diet for short) is low in carbohydrates and fat. It entails substituting a lot of your carbohydrate consumption with fat. When you drastically cut down on carbohydrates, your body enters a metabolic state known as ketosis. In a metabolic state called ketosis, fat is burned very effectively as fuel.

Possible nutritional benefits include:
- Reducing body fat is a primary goal.
- Advantages include lower blood pressure, blood sugar, and HDL cholesterol; improved insulin sensitivity; and decreased HDL cholesterol.
- There is some evidence that following a Keto diet can help with epilepsy.
Plenty of tasty foods can be enjoyed while following the Keto diet. Wild Alaskan also serves as a grocery store, where you can get a wide variety of fish meals. In addition, if you’re seeking meat dishes and food supplies! Excellent food and meat products can be found there.
Potential Benefits of a Low-Carb Diet
⇒ Helpful in reducing body fat
Compared to a calorie-restricted diet, with 30% of calories coming from fat during six months, the BMI drops more dramatically on low-carb diets. The participants in the low-carb group shed an additional 8 pounds, roughly 5 of which were body fat, compared to the participants in the low-fat group, without any adverse effects on cardiovascular risk factors.
Adolescents in the study also demonstrated significant decreases in body mass index (BMI) after 13 weeks of treatment. For this investigation, a low-carbohydrate diet was defined as one with less than 30 percent carbohydrates per day. In this trial, no adverse events occurred, and the teens had no dietary complaints.
Half of the individuals who started the problem did not see it through to the end, which is on pace with the completion rates of people who try the standard low-fat diet.
Since low-carb diets lead to a more significant loss of abdominal fat, they are particularly effective in reducing the dangerous, visceral fat linked to an increased risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
⇒ Enhances Glucose Regulation
Diabetics may be the people who benefit most from a low-carb diet. Blood sugar levels rise after they eat carbs because their cells cannot take in glucose. Extremely high blood glucose levels are dangerous and even fatal.
This is why insulin is a necessity for people with diabetes. The British study found that low-carb diets work just as well for weight loss in diabetic and non-diabetic patients over three months. Patients with diabetes either adopted a low-carb diet or ate what UK nutritionists considered a “healthy” diet to manage their condition.
More weight loss occurred in those who followed the low-carbohydrate diet. Even more impressive, 85% of study participants maintained their diet throughout the experiment. After just one day on a low-carb diet, some people with diabetes can cut their insulin dosage in half.
Some people only need to take their medicine for a few weeks or months before they feel better without it. Hypoglycemia is potentially fatal and was seen to decrease in patients who reduced their drug use.
⇒ Reduces Levels of Triglycerides
While low-fat diets may have unfavorable effects on blood triglyceride levels, research shows that low-carb diets regularly reduce these levels.
Those who successfully lose weight by adhering to the reduced-fat recommendations may find that their blood triglyceride measures remain elevated because of the greater carbohydrate levels often associated with low-fat diet plans.
⇒ Increases Good Cholesterol (HDL)
When this level increases, your body produces more HDL cholesterol, the healthy sort. This HDL subtype is responsible for transporting cholesterol from the body’s periphery back to the liver, where it can be recycled or eliminated.
This reduces the likelihood of cholesterol accumulating in undesirable places, such as the arteries, which can cause plaque buildup. The ratio of good HDL cholesterol to harmful triglycerides is a reliable predictor of cardiovascular disease risk, and low-carb diets increase it. More favorable ratios indicate a more significant potential for preserving cardiovascular health.
⇒ Modifies LDL Cholesterol Distribution Patterns
LDL cholesterol is the only risk factor that doesn’t alter much on a low-carb diet. Although this is commonly referred to as “the nasty kind,” the reality is more complex. There are two forms of low-density lipoprotein (LDL): the former is compact and dense, sometimes compared to BB gun ammunition, while the latter is large and fluffy (think cotton balls).
Because of their small size and high density, LDL particles are easily oxidized (harmful) and can permeate artery walls, ultimately contributing to the development of heart disease.
Therefore, you want fewer BB-like particles and more fluffy ones. In the blood, low-carb diets alter the distribution of LDL cholesterol, decreasing the number of compact, dense particles and increasing the number of large, fluffy ones.
In this way, the prevalence of helpful particles increases, protecting the circulatory system even while LDL cholesterol measurements don’t reduce with low-carb diets.
⇒ It’s in the Body’s Nature to Limit Calories
Satisfaction from low-carb diets is high. People on high-protein, high-fiber diets tend to consume fewer calories per meal than low-fat diets because fats aren’t limited. Consuming protein and fat together will help you feel fuller for longer because they both have a slower digestion rate.
This significantly reduces the need to snack between meals, reducing overall calorie consumption. Because of the more significant satiation effect, portion control is unnecessary on a low-carb diet.
⇒ It helps lower the consumption of inflammatory foods
Obesity, type 2 diabetes, peptic ulcers, asthma, and sinusitis are just a few of the many conditions linked to chronic inflammation, making it a major financial and health problem. Several chronic inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and heart disease, have been linked to foods avoided on a low-carb diet.
The Arthritis Foundation has identified the top 8 inflammatory foods, including sugar and refined grains (typically excluded from low-carb diets). The items recommended for an anti-inflammatory diet are similar to those of a low-carb diet, with the addition of more omega-3 fatty acid-rich foods like fish and nuts.
⇒ Protects Neurological Function
For almost 80 years, people with epilepsy have been able to minimize their seizure activity by following a ketogenic diet, which severely limits their carbohydrate intake. Recent research suggests that a low-carb diet may also be effective in treating Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Further studies are being conducted to see whether or not an extremely low-carb diet can protect individuals recovering from stroke and brain injuries. The chance of acquiring neurological problems may be reduced by following a low-carb diet if doing so helps change aberrant electrical activity in the brain.
⇒ Pays More Attention to Whole Foods
Refined carbohydrate-rich foods can free you up to select from a wide range of healthful whole foods if you’re attempting to reduce weight.
On a low-carb diet, even starchy vegetables can be consumed in moderation as long as they are not overcooked. Due to their higher carb count, white potatoes can be difficult to incorporate, but sweet potatoes and yams are high-fiber alternatives with lower carb counts.
Vegetables low in carbohydrates tend to be rich in diversity, taste, and texture, and many fruits, such as blueberries and grapefruit, are also suitable. The guidelines for low-carb diets propose increasing the intake of these foods to compensate for the “bad” carbohydrates found in refined and processed foods.
The USDA’s food pyramid, which represents healthy eating habits, was recently redesigned into a plate, with half of the space reserved for produce.

⇒ Emphasizes Food Allergies and Weight Gain-Causing Ingredients
Unless you want to go on an elimination diet or spend a lot of money on testing, the only reliable approach to finding out what foods you might have trouble tolerating is to leave them out of your diet for a period and then gradually reintroduce them.
Wheat and sugar are the most typically avoided items when on a low-carb diet; however, this is usually only a temporary measure. It’s hard to ignore the adverse effects of reintroducing refined foods into the diet at a later time.
A person’s experience is a significant motivator for making good dietary choices, regardless of whether they have gluten intolerance or become aware of glycemic changes in response to carbohydrates.
Sugar’s addictive nature isn’t always apparent until after it’s eliminated from the diet and reintroduced. According to a National Institutes of Health survey, the body responds more strongly to sugar and sweet rewards than cocaine. Reactions can be severe and often very uncomfortable when a problem food is removed from the diet and reintroduced.
Following a low-carb diet may prove invaluable if it reveals which foods are hindering your efforts to achieve a healthy weight or improve your health.
⇒ Improves Physical Performance
Studies spanning 20 years show that low-carb diets offer biological outcomes similar to high-altitude training, which is always a goal for athletes. When fat is used for fuel, muscle glycogen reserves are not depleted but remain steady.
Athletes benefit from a more optimal body composition for activities that call for stamina and endurance when they eat a low-carb diet since it allows them to tap into body fat for continuous needs.
Also, Athletes benefit greatly from increased oxygen availability, and low-carb diets make it easier for the body to take in enough oxygen to power peak performance.
⇒ Easier to Follow
Sticking to your diet is the most important part of improving your health through nutrition. Reasons vary, but we all know that failing to stick with a diet plan will prevent us from seeing the results we desire.
However, low-carb diets aren’t the best option for everyone, a recent analysis of nearly 20 different eating programs found that most dieters had tremendous success with a low-carb approach than with a low-fat one.
⇒ You’ll get more out of your gym sessions
Putting it mathematically is a breeze. Protein is essential for optimal muscle growth and recovery after exercise (as you know, it helps promote muscle growth and regeneration). When you consume more carbohydrates, your body has less “room” for protein. Reduce your carb intake to maximize your protein intake.
⇒ You have better chances of experiencing sustained health benefits:
A low-carb diet is more practical in the long run than restrictive fad diets. You may still enjoy food without worrying about calories or going off your diet by eating what you want (in moderation or by making intelligent alternatives). This makes it less challenging to keep up your current standard of living as you age.
⇒ You’ll have fewer sugar cravings overall:
When you eat foods heavy in carbohydrates and sugar, your brain releases feel-good chemicals like serotonin, dopamine, and other soothing endorphins.
A person who experiences the positive impacts of these compounds may be more inclined to seek them out in the future. As a result, eating too many carbohydrates might create a vicious cycle of overeating. You can reduce your dependence on sugar and sweets by eating fewer carb-rich foods, eliminating your desire for them.
Who Should not do a strict Low-carb Diet?
Because of individual differences in metabolism and response to nutrition, not all doctors or health specialists recommend the ketogenic or keto diet. Because of the potential for adverse side effects, the Keto diet shouldn’t be followed by anyone who:
- Has a history of disease or severe health condition.
- Has an eating disorder.
- Is lethargic, skinny, allergic to certain foods, or needs a specific gram of carbs (more than the ideal gram of carbs prescribed in the Keto diet).
Therefore, one should get their blood sugar checked and allergies checked before starting the Ketogenic diet (or any other diet with its tight rules and restrictions) to ensure they aren’t at risk for any rare issues that could harm their health after starting Keto.
The ketogenic diet is not recommended for those experiencing specific health issues.
Because of the potential for these adverse outcomes, individuals with the following health issues should avoid the Ketogenic diet:
- Those Who Are Underweight
Since the Keto diet is low in carbohydrates, and persons who are already underweight or who have recently lost weight due to disease or health concerns may find that they cannot meet their energy needs, it is not recommended that they follow the Keto diet. In addition to this, there may also be some health consequences.
- Individuals who are battling an eating disorder
The Keto diet is very balanced and will not produce any intended benefits if not appropriately followed, which is impossible for those struggling with food disorders because it might be painful for them. In such persons, the Keto diet may lead to psychological distress and physiological imbalances, which may prove lethal in extreme circumstances.
- Underage individuals
Unless a medical condition, such as obesity, requires it, children under 18 should not be required to adhere to a special diet. Adequate intake of lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins, along with all the other nutrients, is essential for children under 18 who are still developing and in the adolescent stage of life. The Ketogenic Diet is a restrictive eating plan that may harm a child’s health and growth.
- Diabetics taking insulin, metformin, or other antidiabetic medicines
Those with extremely high blood glucose levels, type 1 or type 2 diabetes, or who are currently taking Insulin, Metformin supplements, or any other treatment for their condition should avoid the Keto diet at all costs.
It is dangerous for the patient to consume a Ketogenic diet without the doctor’s approval because there are still fewer observations of the Keto supplement’s impact on insulin and metformin doses. Despite this, there is little dedicated research on the topic, and the dietary plans of diabetics and Keto dieters are pretty similar (both are low in carbohydrates).
- Pregnant and lactating women
The ketogenic diet, which is characterized by a low intake of carbohydrates, should be avoided by pregnant women because of the potential harm it could do to their unborn child’s health and growth. There’s also the risk that the mother’s body won’t acquire the nutrition it needs during this time.
After conception, the ketogenic diet can create significant issues for the mother and her unborn child, including developmental delays and nutritional shortages.
However, a low carb consumption during breastfeeding can lead to a hazardous illness called ketoacidosis; hence breastfeeding women are also cautioned against this diet. Ketosis adversely affects milk production because of the metabolic alterations and increased nutritional demands of milking.
- Patients making a comeback after surgery
Since a ketogenic diet promotes the body’s utilization of fat for energy rather than carbohydrates, following such a regimen after surgery will result in the patient losing weight.
Due to the body’s need for all the proper food nutrients throughout the recovery phase, going on the Keto diet right after surgery could cause major deficiency disorders. Therefore, you shouldn’t do that.
Foods to Eat and Avoid:
➤ Foods to Eat
The majority of a high-protein, low-carb diet should be composed of healthy fats, high-quality proteins, and non-starchy vegetables. Here are some low-carb diet-friendly options.
1. Healthy Fats
👉 Butter and ghee; Flaxseed, Macadamia, and Avocado Oil; MCT Oil;
👉 High-Quality Proteins
👉 Fattier cuts of lamb, goat, veal, deer, and other game, as well as grass-fed Beef.
2. Liver and other organ meats
👉 Pheasant, turkey, chicken, quail, hen, goose, and duck are all examples of poultry.
👉 Eggs and egg yolks that have not been kept in a cage
👉 A wide variety of fish, like tuna, trout, anchovies, bass, flounder, mackerel, salmon, sardines, etc.
3. Non-Starchy Vegetables
👉 Cruciferous vegetables, such as cauliflower, broccoli, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts.
👉 Asparagus, bell pepper, mushrooms, water chestnuts, bean sprouts, sugar snap peas, bamboo shoots, radishes, jicama, green beans, wax beans, tomatoes, and many other low-carb vegetables
👉 Avocado (technically a fruit).
4. Full-Fat Milk with Cheese
Full-fat cheeses, butter, and ghee; the full-fat cow and goat milk (preferably organic and raw);
5. Snacks
👉 Additional raw or cooked vegetables with a homemade dressing, Bone broth, Beef or turkey jerky Hard-boiled eggs.
👉 Half an avocado topped with lox (sliced salmon) Lettuce wraps filled with ground pork.
6. Condiments
Ingredients: cocoa powder, vanilla extract, stevia, and various spices and herbs.
7. Drinks
Including water, black and green tea without sugar, freshly squeezed vegetable juice, and bone broth.

➤ Foods to Avoid
Consumption of sugar, refined grains, processed foods, and sugar-sweetened beverages should be restricted while on a low-carb diet. When adhering to a balanced, high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet plan, limiting or avoiding the following foods is crucial.
1. Sugar
👉 Sugar in its various forms: white, brown, cane, raw, and powdered.
👉 A variety of syrups (maple, carob, maize, caramel, and fruit).
👉 A mixture of honey and agave nectar.
👉 Products contain sugars like fructose, glucose, maltose, dextrose, and lactose.
2. Refined Grains
👉 Bread, pasta, cereal, rice, and quinoa.
👉 Popcorn, tortillas, grits, polenta, and cornmeal all contain corn. Bread, bagels, rolls, muffins, pasta, etc., all have flour.
3. Processed Foods
👉 Such as crackers, chips, pretzels, etc.
👉 Sweets of every variety!
👉 Cookies, cakes, pies, and ice cream are included in this category.
👉 Breakfast pastries like pancakes, waffles, etc.
👉 Cereals and rolled oats.
👉 Granola bars, most protein bars, meal replacements, and other high-carb snack foods.
👉 Soups in a can, meals in a box, and other ready-to-eat options.
👉 Sweeteners (sucralose, aspartame, etc.), colors, and tastes added to food in a lab.
4. Caloric Beverages
👉 Carbonated soft drinks Alcoholic beverages (beer, wine, liquor, etc.) Sweetened and coffees.
👉 Fruit juices and milk alternatives Dairy-free yogurts and ice cream.

Example of a Low-carb Meal Plan
There is no need for a healthy, low-carb diet menu to be tasteless and uninteresting. Look at this seven-day meal plan and set of easy low-carb recipes for some motivation to make dietary changes:
Monday
• Breakfast: a vegetable omelet with tomatoes, bell peppers, and spinach.
• You can take Teriyaki salmon with sautéed kale and mushrooms for lunch.
• Have grilled chicken, florets of broccoli, and cauliflower rice for dinner.
Tuesday
• Breakfast of full-fat plain yogurt with blueberries, walnuts, and cinnamon.
• Lunch of veggie burger on a lettuce bun with a side salad.
• Dinner of Mediterranean grilled lamb chops with asparagus.
Wednesday
• Try the crustless spinach quiche for Breakfast.
• For lunch, try the taco salad with ground beef, tomatoes, lettuce, avocados, bell peppers, and salsa.
• Tonight’s dinner features a turkey breast cooked with herbs and Brussels sprouts.
Thursday
• Breakfast: unsweetened coconut flakes, almonds, and coconut chia pudding.
• Lunch: eggplant rollatini with a variety of vegetables.
• Dinner: baked grouper with zucchini fries.
Friday
• Scrambled eggs with tempeh bacon for Breakfast.
• Chicken lettuce wraps with cauliflower fried rice for lunch.
• lamb stew with garlic roasted broccoli make up a typical day’s worth of meals for dinner.
Saturday
• Pancakes that are high in fat and low in carbohydrates for Breakfast.
• Beef, tomatoes, onions, garlic, parsley, and cheese-stuffed bell peppers for lunch.
• Chicken breasts and fried cabbage steaks are tonight’s dinner.
Sunday
• Cinnamon, Greek yogurt, almond milk, blueberries, and vanilla extract make a delicious breakfast smoothie.
• Black olives, Greek salad with spinach, feta, cucumbers, onions, and chickpeas you can take for lunch.

Health Risks of Low-Carb Diets
1. You May Consume More Bad Fats
All lipids are not created equal. Eating more omega-3s and fewer omega-6s is recommended. The risk of cardiovascular disease, cardiac fatalities, and total mortality is lowered by omega-3s. If you unknowingly increase your fat intake, you may consume too much omega-6 and not enough omega-3. Vegetables, nuts, and seeds are the primary food sources of omega-6 fatty acids. Omega-6s are essential fatty acids, but you aren’t getting enough from a diet of plain nuts. Using refined vegetable oil, which is nearly entirely composed of omega-3s, exacerbates the problem.
2. Fruits and vegetables may be lacking.
Fruits and vegetables include nutrients that can be lost when following an extremely low-carb diet. This is especially true if you obtain carbohydrates from unhealthier options like white bread and sweets.
Reduce your consumption of poor-quality carbs until you see improvement. Bread and other carbohydrates are examples. Instead, it would be best if you tried to receive most of your carbs from vegetables and fruits. The calorie and nutritional density of both of these food categories are exceptional.
While on a low-carb diet, you can still consume many vegetables; you’ll have to pick them out of your diet in favor of the cupcake.
3. Consuming Excess Protein
People on a low-carb diet should rely on fat for most of their caloric intake. There are, however, those who choose to consume protein instead. For those trying to lose weight, protein is the best macronutrient to improve your metabolic rate and keep you feeling full longer.
The amino acids in the protein that aren’t used by the body are converted into glucose.
4. Inadequate Fat Intake
In recent decades, there has been a serious campaign to reduce our consumption of fats. In recent years, however, it has become widely accepted that sugar, not fat, is the primary causative factor in weight gain.
Despite this, many worry that they are overeating fat. Pursuing optimal health may lead some to cut back on carbohydrates and fats. But there’s no way this could ever work. Both are necessary for survival, but you can’t have both at once, or you risk malnutrition and, in extreme situations, famine. Protein alone will not sustain life.
5. Not Eating Enough Sodium
The success of low-carb diets can be attributed, in part, to the reduction in insulin levels. Insulin instructs your liver to store salt and your cells to store fat, among its many other functions in the body.
6. Refraining from Indulging
A low-carb diet is a great option for anyone looking to shed pounds. This is because, unlike most other diets, they don’t restrict you from eating items rich in flavor.

Conclusion:
Those with frails or with severe underlying medical issues should also check in with their doctors and nutritionists before making any drastic changes to their diet. Before starting the Keto diet, people should get checked for any diseases or allergies they may have. Finally, all that is important is that you are healthy, regardless of your diet plan.
Although low-carb diets have been attacked from all sides for years and are even called a “fad diet,” the most recent scientific evidence does not back these claims. You can improve your health and still eat well on a low-carb diet; you must be more mindful of your portions. There are a plethora of free fitness tracking services out there.
Most of them may be used with minimal effort and provide helpful information like the user’s weight, the foods they ate, the number of calories they burned, etc. Some apps connect to smartwatches and other wearable fitness trackers, and others can be found on the internet.





