Mirena Side Effects: Does It Cause Weight Gain?

The age of unwanted pregnancy and abortions no longer exists. Mirena IUD has revolutionized the birth control arena with its innovative and breakthrough technology. Now you can replace 2,920 daily birth control pills over 8 years with a single Mirena IUD.
Along with the hype of this IUD, an alarming concern is also on the rise. It is whether the IUD will cause weight gain or not. Even though there is a misconception that IUDs cause weight gain, the fact is not at all unilateral.
Jump right into the article to know Mirena and whether it will cause weight gain or not.
What Is An Intrauterine Device?
IUD aka Intrauterine Device is a small, T-shaped device that can be put inside your uterus to prevent pregnancy. FDA has approved five different brands of IUDs in the United States namely, Paragard, Kyleena, Liletta, Skyla, and Mirena.
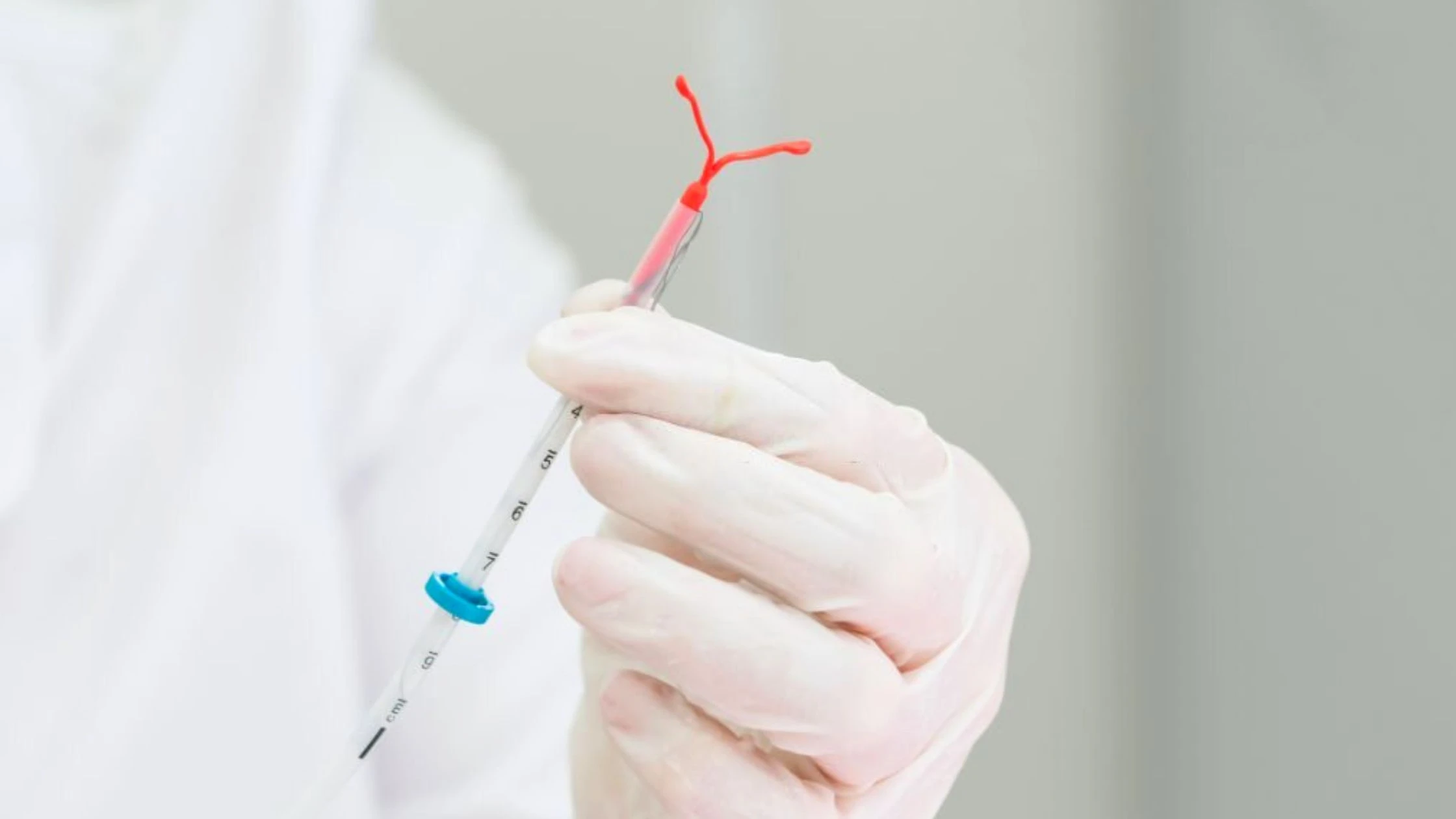
These devices are also known as IUC aka Intrauterine Contraception. There are two types of IUDs. They are listed below:
- Hormonal IUDs – Kyleena, Mirena, Skyla, Liletta, etc.
- Copper IUDs – Paragard
Hormonal IUDs use the hormone progestin to prevent you from getting pregnant. While copper IUDs don’t have any hormones attached.
What Is Mirena?
Mirena is the brand name of an Intrauterine Device (IUD), that can prevent unwanted pregnancy and also treat heavy periods. It can prevent pregnancy for up to 8 years and treat heavy periods for up to 5 years.
The scientific name of Mirena is levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system. It is one of the number one prescribed intrauterine devices in the United States. Studies have shown that Mirena can provide 99% effectiveness in preventing pregnancy.
It is the first and only hormone-releasing IUD approved by FDA to treat heavy periods known as HMB (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding). This IUD can be used even if you have a baby or not.
How does Mirena’s IUD work?
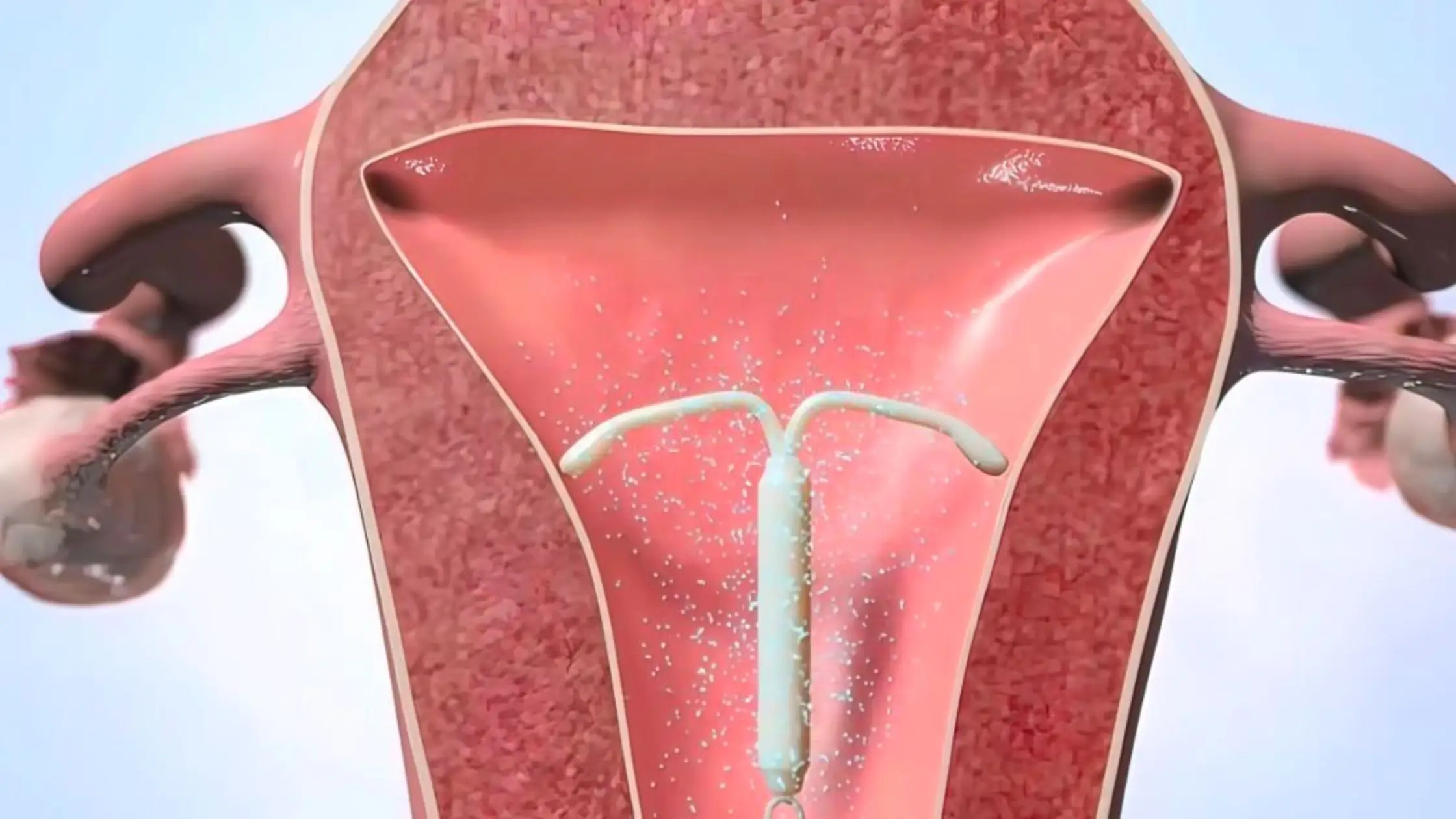
Like any IUD, Mirena is placed inside your uterus by a healthcare provider or medical expert. It contains 52mg of a hormone known as levonorgestrel, a type of progestin used in birth control pills.
While Mirena is inside your uterus, it releases small doses of levonorgestrel inside your bloodstream. The hormones released inside the uterus thicken the cervical mucus and prevent sperm from entering. Also, it has properties that can resist sperm movement so that sperm cannot reach your uterus.
Another way the Mirena works to prevent pregnancy is by thinning the inside lining of the uterus. This will resist the egg to the walls of your uterus.
Who should not use Mirena?
Mirena cannot be used by everyone. You have to check on certain aspects before using this Intrauterine Device. Some of the categories of people who shouldn’t use Mirena are listed below:
- People who are or might be pregnant.
- People with pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- People with untreated genital infection
- People who are susceptible to infections
- People with a probability of cervical or uterus cancer
- have vaginal bleeding
- Have liver disease
- Breast cancer or other cancers
- People with an already IUD
- have fibroid tumors
- has an allergy to levonorgestrel, silicone, silica, polyethylene, etc
Common side effects of Mirena
There are some common side effects of placing Mirena inside the uterus. Some of these are listed below:
- Pain and bleeding after placing the device: If you experience pain, dizziness, and bleeding after placing Mirena inside the uterus, it might be misplaced. Contact your healthcare provider if those symptoms don’t last even after 30 minutes.
- Changes in menstruation: This is a common side effect of using a Mirena IUD. Sometimes this is characterized by heavy bleeding and sometimes blood can be spotted between periods.
- Lack of menstrual periods: Studies show that 2 out of 10 women stop having periods after one year of IUD use. If you are worried that you might be pregnant, contact your healthcare professional.
- Temporary cysts: Another common side effect of using a Mirena IUD is the emergence of temporary cysts. These can appear within 2 to 3 months of IUD installation. Sometimes these cysts can cause pain and might need surgery for removal.
- Pelvic or abdominal pain: Sometimes using Mirena can cause pelvic or abdominal pain.
- Vulvovaginitis: This is a condition characterized by inflammation or infection of the external region of the vagina.
- Vaginal discharge: In some cases, using Mirena IUD can cause vaginal discharge as one of the side effects.
What are the long-term risks?
While using the Mirena IUD, there is a chance of some long-term risks too. If you experience any of these risks, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
- Ovarian Cysts: Ovarian cysts are a risk factor associated with using Intrauterine Devices such as Mirena. They are symptoms of abdominal pain and swelling. Nausea, painful bowel movements, painful menstruation, etc are some of the symptoms of this condition.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): This affects your reproductive organs. Studies show that there is a risk factor of developing a PID after the first 3 weeks of an IUD insertion.
- Expulsion: There is a chance that your uterus can expel the IUD. Or it can get stuck around the wrong position. So it is recommended to check the position of your IUD once a month.
- Perforation: This is an unlikely chance, still Mirena can perforate the walls of the uterus if not placed properly.
- Pregnancy: There is only a 0.2 percent chance of getting pregnant while you are on Mirena.
Can Mirena Induce Weight Gain?
There are many misconceptions regarding the association between Intrauterine Devices and weight gain. Being a hormonal IUD, there is a chance that Mirena can cause weight gain even for a slight percentage.

But the fact is that no proper research has been made regarding this. Studies have shown that progestin, a hormone in the Mirena IUD can cause weight gain. It works by increasing the water retention in your body and thereby aiding in weight gain.
But there is no valid evidence from research regarding how much weight is gained from using these IUDs or whether they are the result of this. Right now we have only anecdotal evidence of weight gain and the connection between progestin and weight.
Apart from that, no valid study has been made regarding the connection between IUDs and weight gain.
Also read: Estrogen-Induced Weight Gain: How Estrogen Contributes To Weight Gain?
Conclusion
Intrauterine Devices have revolutionized the birth control strategy. They are effective and can be applicable for long-term usage. Mirena is the brand name of a hormonal IUD based on levonorgestrel.
It has a 99% success rate in preventing unwanted pregnancy and also reducing heavy blood flow during menstruation. Still, there are many side effects of using this IUD. And one common conception is that Mirena can cause weight gain.
Even though hormones can cause weight by increasing fluid retention, there is no solid proof regarding the weight gain effect of IUDs. Much research has to be conducted in this area to finalize the relationship between Mirena and weight gain.
FAQs
You can use it for 8 years to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
You should check if the place is correct once every month.
Yes. But consult your doctor before using it.
Yes. There is no problem in using tampons and menstrual cups along Mirena.
Yes. There might be pain and bleeding. But if these symptoms don’t pass within 30 minutes contact your healthcare provider immediately.





