What Are The Risk Factors Of Obesity On COVID 19 Complications?
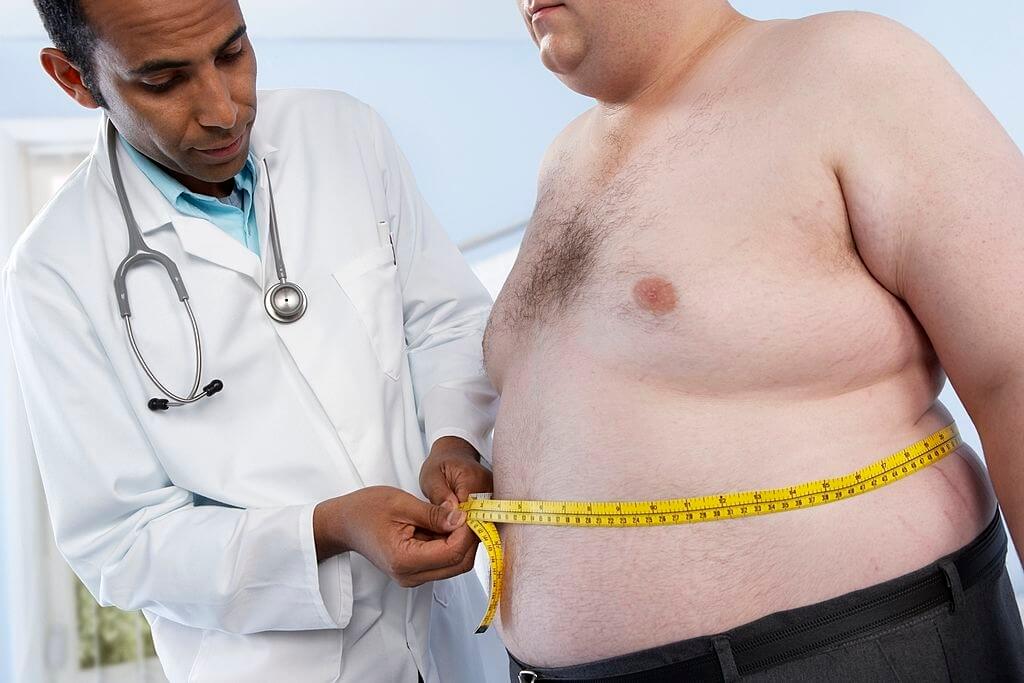
Obesity is defined as a condition in which a person has an unhealthy quantity of body fat or a harmful fat distribution. It puts you at risk for a variety of severe health problems. Bones and organs are strained by excess body fat.
What Are The Risk Factors Of Obesity On COVID?
Extra weight is linked to various chronic illnesses, making you more prone to have COVID-19 problems. Obese people are at a higher risk for various health problems, including chronic illness, infection, and delayed wound healing. Another health concern to be mindful of these days is the rise of COVID-19 consequences, a respiratory disease caused by a new coronavirus.

Obesity Is A Risk Factor For Viral Pandemics, And Obese Infected Individuals Have A Poorer Prognosis.
COVID-19 is no exception, and Public Health England has released a study on the link between obesity and COVID-19.140 Individuals with obesity, particularly those with morbid obesity (BMI > 40 kg/m2), should be considered as one of the clinically susceptible populations during pandemics. To better understand the impact of obesity on pharmacokinetics, clinical trials of medical items should include individuals with obesity. Further study into vaccination regimens is needed to develop and sustain improved immune responses in individuals with obesity to future viral exposure.
High Chances Of Covid Transmission
Compared to individuals in the healthy weight range, people who died with COVID-19 were 1.5 times more likely to be obese than those who survived the illness.COVID-19 victims were 1.5 times more likely to be obese, having a BMI of above 30 kg/m2. 23 When demographic variables including age, sex, and socioeconomic position were considered, the correlations persisted.
High Mortality Rate
Obesity-related chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes, may be blamed for the higher mortality from COVID-19 in obese individuals. Cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes, autoimmune illness, and oral steroid usage were all independently linked with COVID-19 mortality, according to extensive prospective research that carefully investigated the relationships between various clinical risk factors for COVID-19 mortality.
In this research, obesity was not shown to be linked with death on its own. These findings suggest that the higher COVID-19 mortality risk associated with obesity may be attributable to obesity-related diseases, including cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Obese People Are More Likely To Be Diagnosed With Covid-19.
Those who are obese are more likely to be diagnosed with COVID-19 than those in a healthy weight range. Obese individuals were more likely to test positive for COVID-19 that utilized pre-existing data from primary care databases and biobanks. 1516 Obese individuals had a 1.41 to 1.55 times higher chance of testing positive for COVID-19 than those who are in a healthy weight range, according to this research. The biological processes that underpin this finding are presently being researched.
What Can be Done
Obesity is a complex illness with many underlying causes. Obesity may be influenced by neighborhood design, availability of nutritious, inexpensive foods and drinks, and access to safe and accessible venues for physical exercise. This will include policy and institutional changes to guarantee that obesity prevention and treatment begins at a young age. Everyone has access to healthy foods and safe places to exercise.
Policymakers and community leaders must work together to ensure that their communities, surroundings, and systems encourage everyone to live a healthy and active lifestyle.
Given the very high prevalence of obesity throughout the world, we anticipate that a large proportion of those infected with coronavirus will have a BMI of over 25. Patients with obesity who become ill and require intensive care face additional challenges in patient management, as it is more difficult to intubate obese patients, obtaining diagnostic imaging can be more difficult (due to weight limits on imaging machines, patients are more difficult to position and transport by nursing staff, and they, like pregnant patients in ICUs, may nephrotic syndrome.
You May Also Read More: Does Obesity Causes A Higher Risk Of Infection For COVID-19





